Variable Sets
A common use case for tests is to assert the same behavior across multiple environments (dev, staging, and production, for example). To make sure all of these environments will have the same behavior, it is important that the tests executed against those environments test the same aspects.
To reduce the risks of diverging tests, Tracetest allows you to organize different environments configurations using global objects called Variable Sets.
For details on creating and editing varaible sets in the CLI, please visit CLI Creating Variable Sets.
For details on creating and editing varaible sets in the Web UI, please visit Web UI Creating Variable Sets.
Secrets Management
Variable Sets can accept secrets. A variable can be a secret or a raw variable in the Web UI and CLI.
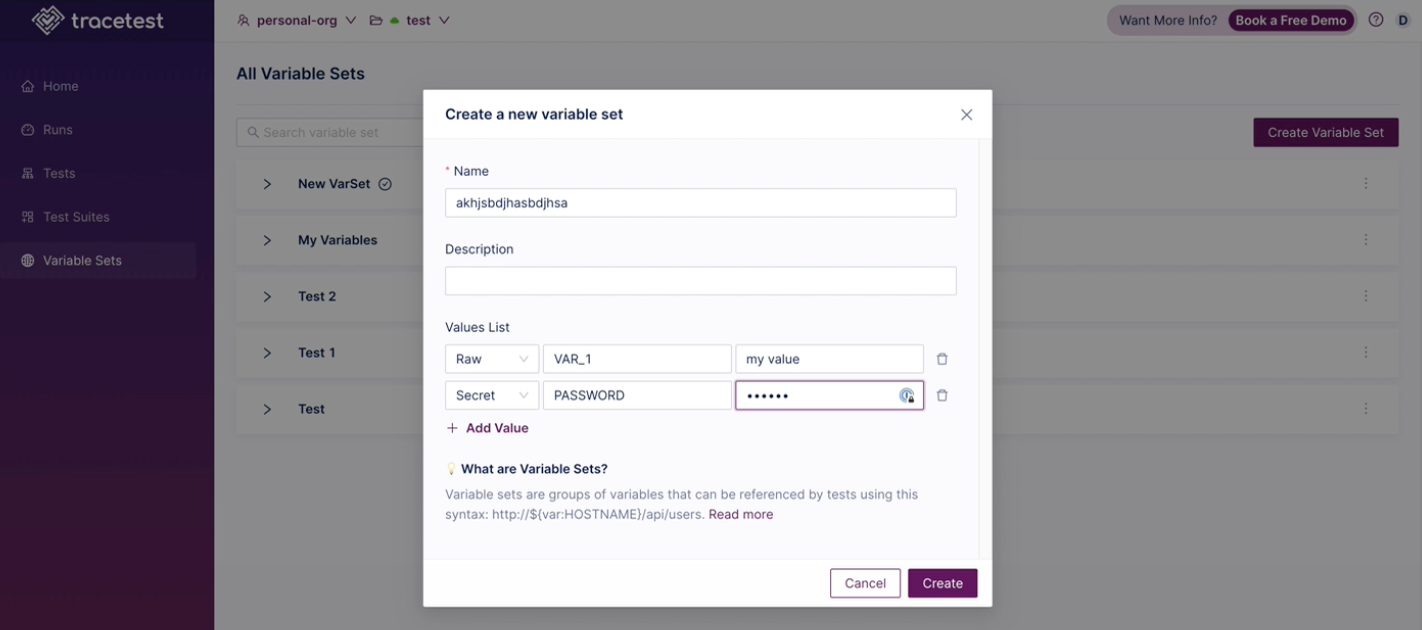
type: VariableSet
spec:
id: test-1
name: Test 1
description: test
values:
- key: SOME_SECRET
value: my-precious
type: secret
- key: NO_SO_SECRET
value: aha!
type: raw
tracetest apply variableset -f <variableset.yaml>
How Variable Sets Work
Variable sets are objects containing variables that can be referenced by tests. You can use a single test and provide the information on which environment object will be used to run the test. To illustrate this, consider an app that is deployed in three stages: dev, staging, and production. We can execute the same test in all those environments, however, both URL and credentials change from environment to environment. To run the same test against the three deployments of the app, you can create three variable sets:
# dev.env
type: VariableSet
spec:
name: dev.env
id: dev.env
values:
- key: URL
value: https://app-dev.com
- key: API_TOKEN
value: dev-key
# staging.env
type: VariableSet
spec:
name: staging.env
id: staging.env
values:
- key: URL
value: https://app-staging.com
- key: API_TOKEN
value: staging-key
# production.env
type: VariableSet
spec:
name: production.env
id: production.env
values:
- key: URL
value: https://app-prod.com
- key: API_TOKEN
value: prod-key
Now consider the following test:
type: Test
specs:
name: Test user creation
trigger:
type: http
httpRequest:
url: "${var:URL}/api/users"
method: POST
body: '{}'
authentication:
type: bearer
bearer:
token: "${var:API_TOKEN}"
Both var:URL and var:API_TOKEN would be replaced by the variables defined in the chosen variable set where the test will run. So, if the chosen variable set was dev.env, its values would be replaced by https://app-dev.com and dev-key, respectively.